Guo Ai - Project Portfolio
Overview
termiNus is an interactive task manager for students in NUS.
Summary of Contributions:
Code Contributed
Enhancement implemented:
- Features added to Task List
- Implement the
categorycommand.- Allow users to set the category of a task.
- Implement the listing sorted tasks feature.
- Allow users to list the tasks sorted firstly by priority in ascending order (high-priority tasks are displayed first). If multiple tasks have the same priority, they are sorted based on category lexicographically.
- Implement the
- Features added to Expense List
- Implement the
spendcommand.- Allow users to add an expense item with a value to the expense list.
- Allow users to optionally label expense items with currency and date.
- Implement the
list expensescommand.- Allow users to list all the expense items in the expense list.
- Allow users to see the summary of the total amount of expenses spent for each currency, and for date ranges including today, this week, this month, and this year, for all the expense items in the expense list.
- The listed expense items listed are sorted.
- First sort based on date in descending order (i.e. the latest expense items are shown first).
- If multiple expense items have the same date, sort them based on currency lexicographically.
- Implement the
list expenses <optional arguments>command.- Allow users to list all the expense items with a specified currency, date, or date range (i.e.
DAY,WEEK,MONTH,YEAR). - Allow users to see the summary of the total amount of expenses spent for each currency for all the listed expense items.
- The expense items listed are sorted.
- Allow users to list all the expense items with a specified currency, date, or date range (i.e.
- Implement the
deletecommand.- Allow users to delete:
- One expense item identified by index from the expense list.
- One or multiple expense item(s) with a specified currency or date from the expense list.
- Display the deleted expense item(s).
- Allow users to delete:
- Implement the
- Features added to all the 5 Item Lists (i.e. Task List, Expense List, Module List, Link List, Book List)
- Implement the
findcommand.- Allow users to search for items (i.e. tasks, expenses, modules, links, books) whose description contains the keyword(s) specified.
- If the input keyword contains only one word (i.e. no whitespaces), match the description of items using the entire word. The keyword must be a whole word in the description.
- If the input keyword contains multiple words separated by whitespaces, in order for the item to be matched, the entire keyword string must appear in the item description, and each individual word in the keyword string must also be a whole word in the item description.
- Implement the
- Write JUnit tests to test the features.
- Provide a skeleton codebase based on my ip. Almost all the functionalities changed, but the basic structure for commands, storage, UI, runner, and exception did not change.
- Refactor code and build a structure for classes.
- Refactor the previous
TaskandTaskListclasses into superclassesItemandItemList. - All other Items (i.e.
Task,Expense,Module,Link,Book) and Item Lists (i.e.TaskList,ExpenseList,ModuleList,LinkList,BookList) inherit fromItemandItemListclasses. - This design is used among all the features and incorporates more OOP principle.
- Refactor the previous
- Follow software engineering principles
- Apply SLAP principle, DRY principle, facade design pattern when implementing features.
- Use functional programming and improve readability when writing code as much as possible.
Contributions to User Guide:
- Add user guide sections for all commands related to expenses
spendcommandlistcommand and subcommandsdeletecommand and subcommands
- Add user guide sections for
findcommand
Contributions to Developer Guide:
- Add a sequence diagram for
Stroagegenerated with PlantUML. - Add a class diagram for
Itemclass and its subclasses. - Explain usage for the
Storagecomponent. - Explain the
Itemclass and its subclasses. - Describe implementation details of
listcommand for expenses anddeletecommand.
Contributions to Team-based tasks:
- Set up the GitHub team organization and invite teammates
- Set up the GitHub team repository
- Refactor code and build a structure for classes
Itemand its subclassesItemListand its subclasses
- Add issues to issue tracker, assign teammates, and add labels
- Smoke test on some features.
Review/mentoring contributions:
- Review, approve, and merge some of teammates’ PRs.
- Example: #184
- Communicate and explain the refactoring about
ItemandItemListand their subclasses to teammates in group chat, so that more OOP can be applied. - Provide details when creating PR to inform teammates of the updates.
- Example: #214
Contributions beyond the project team:
- Create and host weekly project meetings
Contributions to the User Guide (Extracts)
Adding an expense item: spend
Add an expense item into the expense list.
Format: spend <description> <compulsory arguments> <optional arguments>
List of <compulsory arguments>:
v/<value>sets the amount of money spent.
🚩: value has a limit of 100 trillion (100,000,000,000,000).
🚩: value must be non-negative.
List of <optional arguments>:
currency/<currency>sets the currency of the expense.date/<yyyy-MM-dd>sets the date of the expense.
🚩: By default, the currency is set to “SGD” and date is set to the date when the user executes the spend command.
🚩: currency is user defined. It does not have to be a legal currency in the world.
🚩: Optional and compulsory arguments can be typed in any order.
Example of usage:
spend lunch v/5
spend lunch v/5 currency/CNY
spend lunch v/5 date/2020-10-28
spend lunch v/5 date/2020-11-08 currency/USD
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Got it. I've added this expense item:
lunch (5.00 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
Now you have 9 expense items in the list.
____________________________________________________________
Displaying expense items on list: list expenses
List all the expense items in the expense list and shows total amount of money spent for each currency and the current day, week, month, and year.
Format: list expenses
🚩: Expense list is sorted based on date (from the most recent to the least recent). If the date of two expense items are the same, the expense list is sorted based on currency lexicographically.
Example of usage:
list expenses
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Here are the expense item(s) in your list:
dinner (0.60 A) (date: Monday, November 9, 2020)
breakfast (0.10 SGD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
book (0.50 SGD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
bread (0.20 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
lunch (5.00 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
bottle (3.00 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
pen (1.00 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
earphone (0.30 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
tablet (0.40 USD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
Your total expense for today is:
0.60 SGD
5.20 USD
Your total expense for this week is:
4.90 SGD
5.60 USD
Your total expense for this month is:
0.60 A
4.90 SGD
5.60 USD
Your total expense for this year is:
0.60 A
4.90 SGD
5.60 USD
____________________________________________________________
Displaying expense items by a certain currency on list: list expenses (by currency)
List all the expense items in the expense list based on currency and shows total amount of money spent for each currency.
Format: list expenses currency/<currency_name>
🚩: currency_name is case-sensitive.
Example of usage:
list expenses currency/USD
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Here are the expense item(s) in your expense list of currency USD:
bread (0.20 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
lunch (5.00 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
tablet (0.40 USD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
The total amount listed:
5.60 USD
____________________________________________________________
Displaying expense items on a certain date on list: list expenses (by date)
List all the expense items in the expense list based on the date and shows total amount of money spent for each currency.
Format: list expenses date/<YYYY-MM-DD>
Example of usage:
list expenses date/2020-11-08
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Here are the expense item(s) in your expense list of date Sunday, November 8, 2020:
breakfast (0.10 SGD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
book (0.50 SGD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
bread (0.20 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
lunch (5.00 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
The total amount listed:
0.60 SGD
5.20 USD
____________________________________________________________
Displaying expense items for a certain time period on list: list expenses (by time period)
List all the expense items in the expense list based on the time period and shows total amount of money spent for each currency.
Format: list expenses for/<time period>
🚩: <time period> can only be day, week, month, or year.
🚩: time period is case-insensitive.
Example of usage:
list expenses for/week
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Here are the expense item(s) in your expense list for this week:
breakfast (3.00 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
bus (1.00 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
pencil (0.30 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 8, 2020)
pen (0.40 USD) (date: Saturday, November 9, 2020)
The total amount listed:
4.30 SGD
0.40 USD
____________________________________________________________
Deleting an expense item from the list: delete expense
Delete an expense item from the list.
Format: delete expense <expenseIndexNumber>
🚩: <expenseIndexNumber> corresponds to the index given on list expenses command output.
Example of usage:
delete expense 2
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Noted. I've removed all these expense item(s)
breakfast (0.10 SGD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
____________________________________________________________
Deleting all the expense items of a certain currency: delete expenses (by currency)
Delete expense items of the same currency.
Format: delete expenses currency/<currency_name>
🚩: currency_name is case-sensitive.
Example of usage:
delete expenses currency/SGD
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Noted. I've removed all these expense item(s)
earphone (0.30 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
pen (1.00 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
book (0.50 SGD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
bottle (3.00 SGD) (date: Saturday, November 7, 2020)
____________________________________________________________
Deleting all expense items of the same date: delete expenses (by same date)
Delete expense items of the same date.
Format: delete expenses date/<yyyy-MM-dd>
🚩: date argument must be in the format of yyyy-MM-dd, e.g. 2020-11-08.
Example of usage:
delete expenses date/2020-11-08
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Noted. I've removed all these expense item(s)
bread (0.20 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
lunch (5.00 USD) (date: Sunday, November 8, 2020)
Searching for an item with keyword: find
Finds all items in the corresponding item list with matching description.
Format: find {tasks,links,books,expenses,modules} k/<keyword>
🚩: <keyword> is case-insensitive.
🚩: <keyword> can be a single word or a phrase.
🚩: <keyword> must contain whole words from the item description, e.g tp meeting, ip etc.
🚩: Incomplete keywords will not be matched. e.g mee, t etc.
🚩: <keyword> for finding modules or links can only be the related module name.
Example of usage:
find tasks k/tp meeting
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Here are the matching items in your list:
1.[T][N] tp meeting (p:0) (category: cs2113)
2.[T][N] tp meeting 2 (p:0)
____________________________________________________________
find expenses k/dinner
Output:
____________________________________________________________
Here are the matching items in your list:
1.dinner (0.60 A) (date: Monday, November 9, 2020)
____________________________________________________________
Contributions to the Developer Guide (Extracts)
Storage
This section describes how the Storage class works
High level description
Methods handling data loading (i.e. loadTask(), loadBook(), loadLinks(), loadModule(), loadExpense() methods)
return an ArrayList of items (i.e. Task, Book, Link, Module, Expense). These will be the initial values of
the item list (i.e. TaskList, BookList, LinkList, ModuleList, ExpenseList). The save() method takes an
inherited instance of ItemList and a String specifying the path to which the file will be saved. The ItemList will
be parsed and saved into files (each ItemList will be saved to a separate file) at the specified path.
Formats of the files:
tasks.txt:
There are 6 fields stored for each Task:
- String
Tfor “Task” - Whether the
Taskhas been done or not (1 for done, 0 for not done) - Description of the
Task - Priority of the
Task(an Integer) - Category of the
Task - Date of the
Task
All the fields are separated by | with a leading and a trailing space. Each Task is stored as one line.
Example: T | 0 | borrow book | 1 | book | 28-10-2020
books.txt:
There are 5 fields stored for each Book:
- String
Bfor “Book” - Whether the
Bookhas been returned or not (1 for returned, 0 for not returned) - Name/Description of the
Book - Borrow date of the
Book - Return date of the
Book
All the fields are separated by | with a leading and a trailing space. Each Book is stored as one line.
Example: B | 0 | cooking book | 11-11-2011 | 11-12-2011
links.txt:
There are 3 fields stored for each Link:
- Module of the
Link - Use of the
Link - URL of the
Link
All the fields are separated by | with a leading and a trailing space. Each Link is stored as one line.
Example: CS2113 | lecture | https://cs2113Lecture.zoom.com
modules.txt:
There are 4 fields for each Module:
- Module code
- Grade
- Modular credits
- Academic year and semester
All the fields are separated by | with a leading and a trailing space. Each Module is stored as one line.
expenses.txt
There are 4 fields for each Expense:
- Description
- Value
- Currency
- Date
All the fields are separated by | with a leading and a trailing space. Each Module is stored as one line.
Currency has default value “SGD”.
Date has default value of the date that the spend command is executed.
Date will be in the format of yyyy-MM-dd, e.g. 2020-11-09.
Implementation details
The following sequence diagram shows how the Storage works.
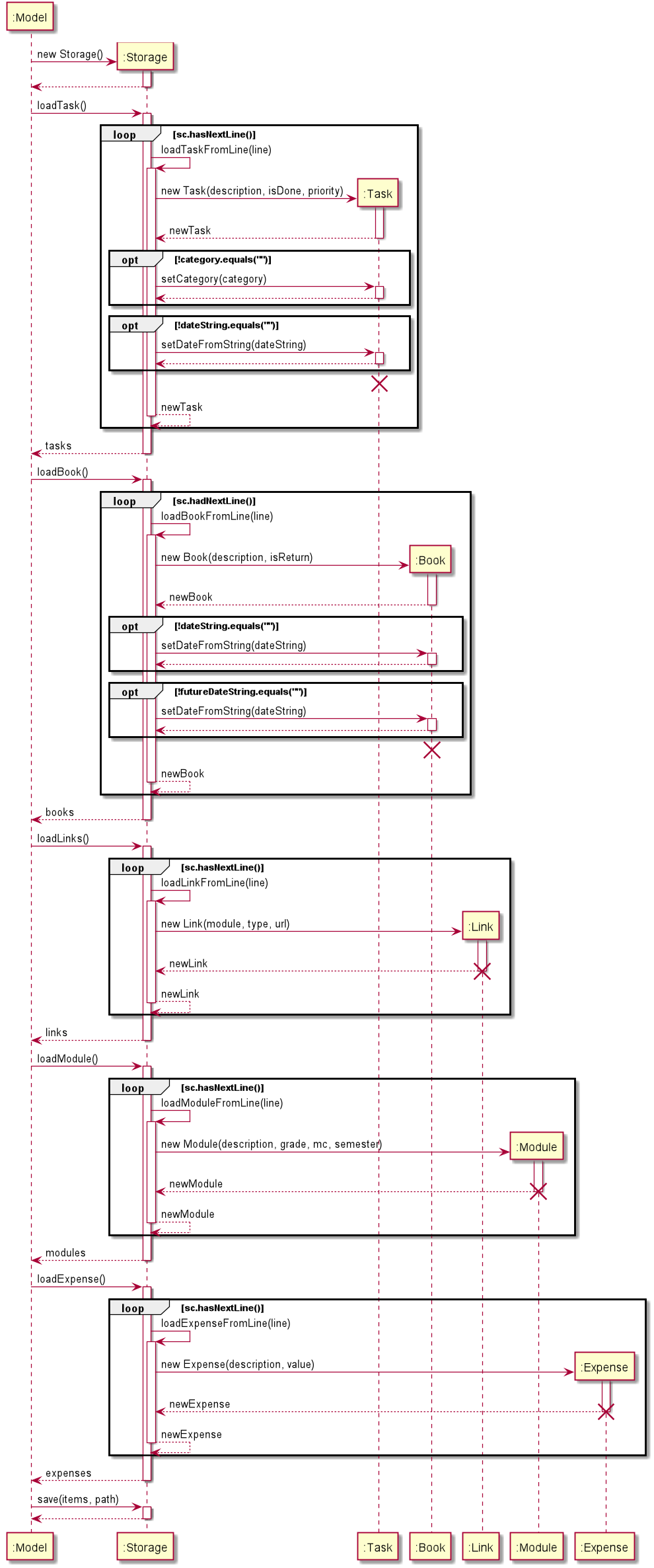
- At the start of
Duke, a newStorageobject will be created. Dukecalls loading methods (i.e.loadTask(),loadBook(),loadLinks(),loadModule(),loadExpense()) sequentially. Each loading method calls the corresponding helper method (i.e.loadTaskFromLine(),loadBookFromLine(),loadLinkFromLine(),loadModuleFromLine(),loadExpenseFromLine()) to loadItems from each line in the file.- After each command,
Dukecalls thesave()method ofStorageto save all theItems in the list to files.
Item component
Item is a super class with 5 subclasses inheriting it: Task, Expense, Module, Link, Book.
Here is the class diagram for Item class and its subclasses.
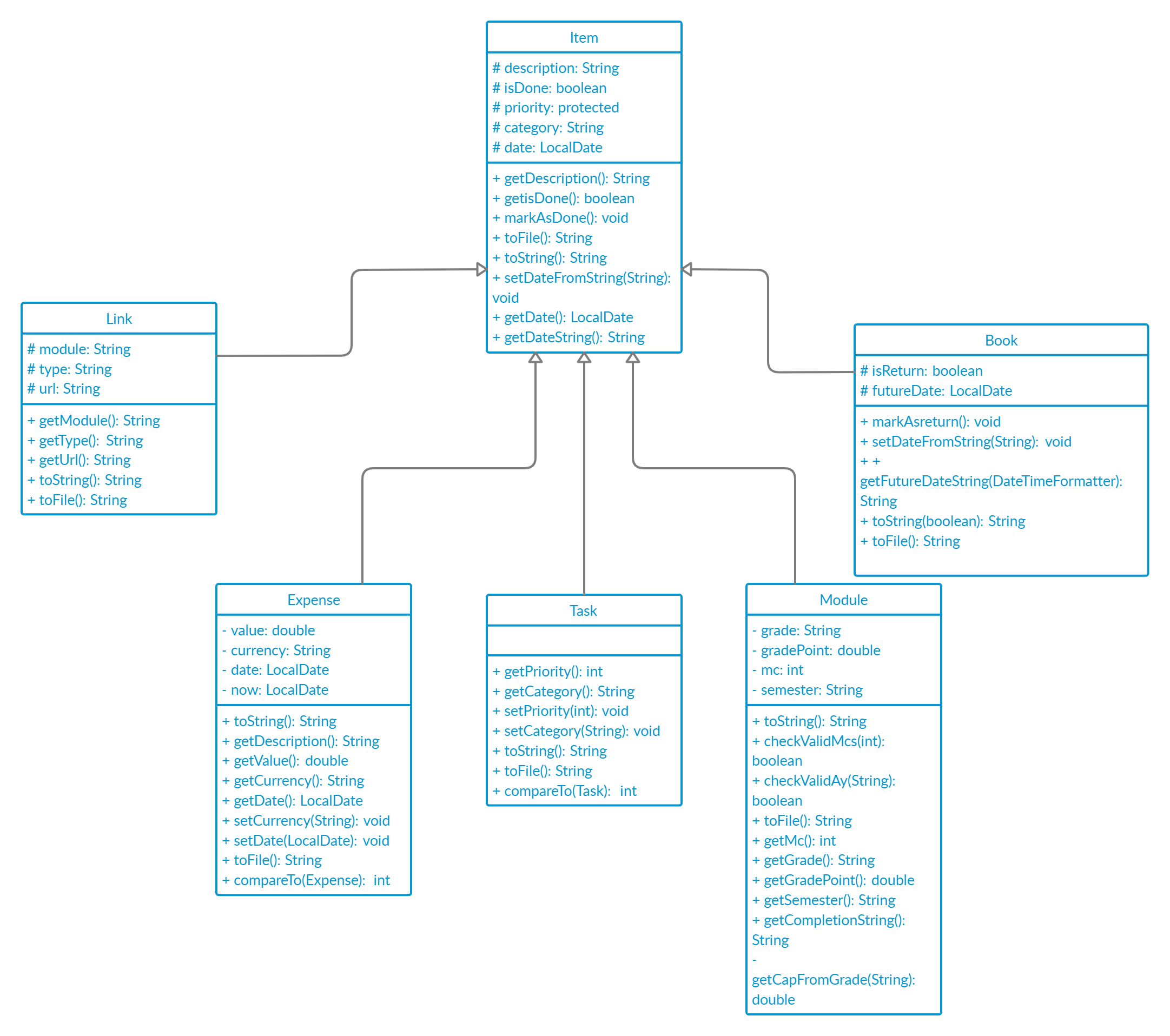
The Item class and its subclasses:
- Contains getters and setters to retrieve and set the attributes.